C++ Online Test
For jobseekers
Practice your skills and earn a certificate of achievement when you score in the top 25%.
Take a Practice TestFor companies
Screen real C++ skills, flag human or AI assistance, and interview the right people.
About the test
The C++ online test assesses knowledge of programming in the C++ language and commonly used parts of the C++ Standard Library. This test requires solving live coding problems in C++.
The assessment includes work-sample tasks such as:
- Implementing and properly using algorithms and data structures to optimize application performance.
- Optimizing memory management and fixing memory leaks.
- Working with OOP principles and higher-order functions to write reusable code.
A good C++ developer needs a solid understanding of the C++ programming language and the ability to take advantage of the functionality provided by the Standard Library to write robust and maintainable code.
Sample public questions
Your company is analyzing malware that targets numerical record files stored in an array.
The malware adjusts values at both the edges of the array using a window of size 's' as shown in the video below:
Implement the simulate method so that the malware behavior is replicated for further study.
A gaming company is working on a platformer game. They need a method that will compute the character's final speed, given a map and a starting speed.
The terrain on which the game character moves forward is made from various pieces of land placed together. Implement the method calculateFinalSpeed which takes the initial speed of the character, and an array of degrees of inclination that represent the uneven terrain.
The speed of the character will increase or decrease proportionally to the incline of the land, as shown in the image below:
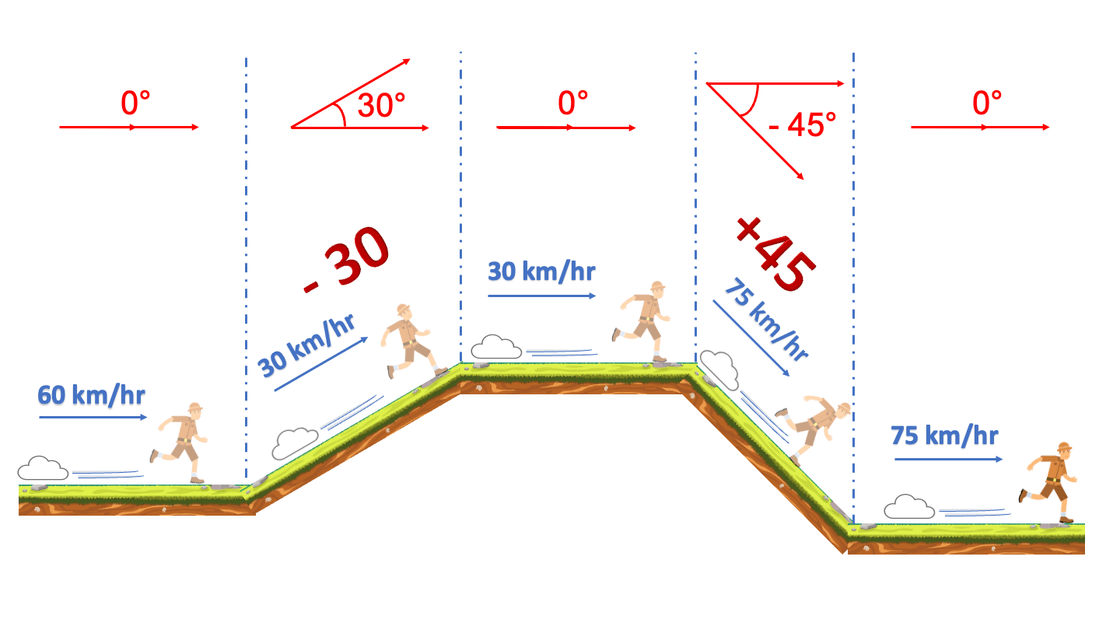
The magnitude of the angle of inclination will always be < 90°. The speed change occurs only once for each piece of land. The method should immediately return 0 as the final speed if an incline reduces the speed to 0 or below 0, which makes the character lose 1 life.
For example, the below code:
std::cout << GamePlatform::calculateFinalSpeed(60.0, { 0, 30, 0, -45, 0 });should print:
75For jobseekers: get certified
Earn a free certificate by achieving top 25% on the C++ test with public questions.
Take a Certification TestSample silver certificate
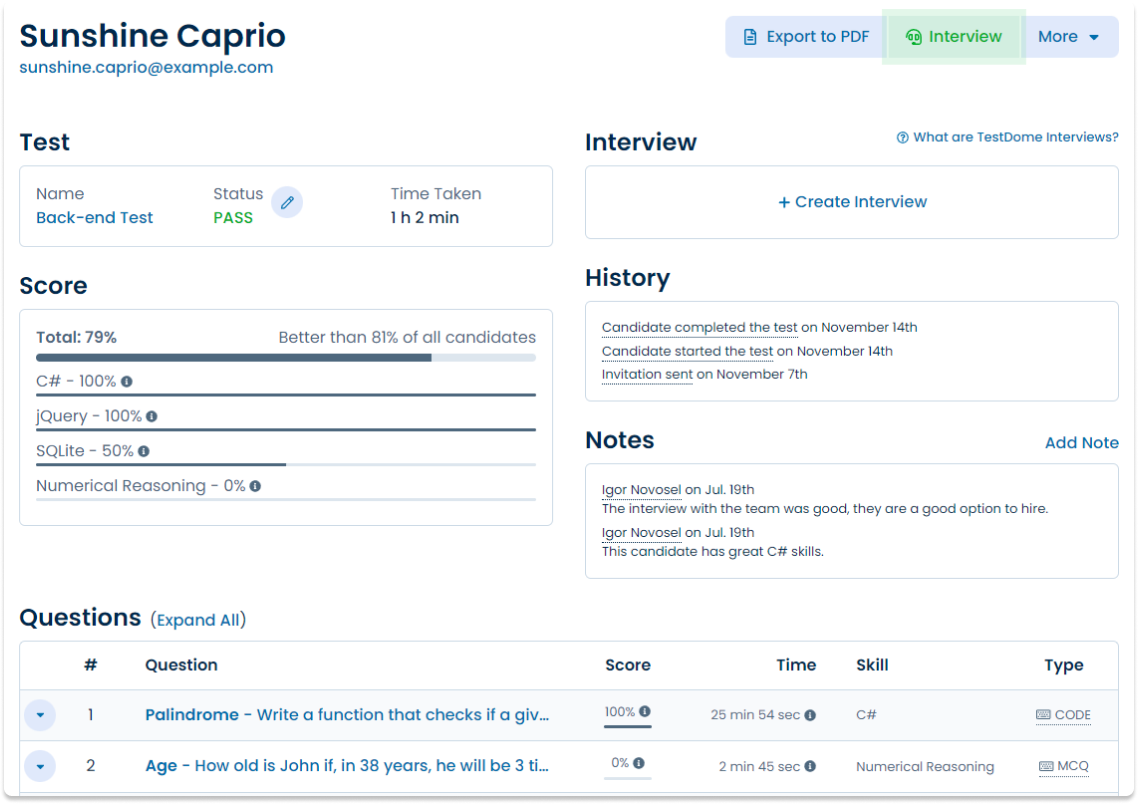
Sunshine Caprio
Java and SQL TestDomeCertificate
For companies: premium questions
Buy TestDome to access premium questions that can't be practiced.
Ready to interview?
Use these and other questions from our library with our
Code Interview Platform.
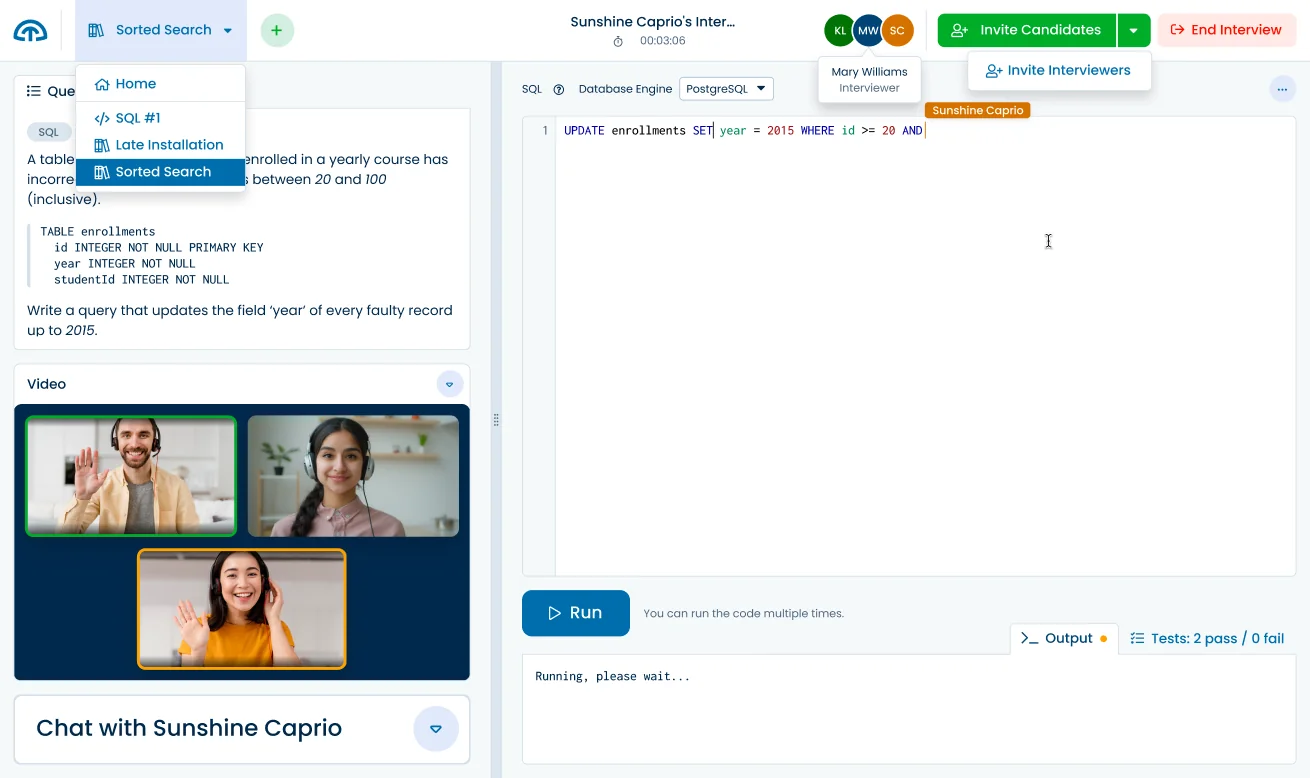
63 more premium C++ questions
Non Zero, Max Sum, Unique Numbers, Increment, Crop Ratio, Internal Nodes, Segment, Tiles, Friend, Fire Dragon, Battery, Weighted Average, Paper Strip, Kilometer Converter, Function Cache, Veterinarian, Hobbies, Out of Range, String Occurrence, Worker, Stories, Username, Window Manager, Document Store, Read Write Execute, Limits, Ship, Book Sale, Unique Product, Stack to Vector, Language Teacher, Sort Params, Read First Line, Vectors, Archive, Paragraph, Procedural Generator, Node, Calories Burned, Babushka Doll, Date Transform, Platformer, Company Stock, Chemical Machine, Seasonal Tourism, Candies, Digital Flasks, Shipping, Patient Class, Automated Forklift, Flimsy Bridge, Construction Game, Parking Allocation, Planet Search, Ecological Experiment, Circuit Simulator, Airport Networks, Chain Link, Moving Total, Flight Connections, Adventure Game, Jobs Time, Christmas Lights.
Skills and topics tested
- C++
- Bug Fixing
- Language
- Algorithmic Thinking
- Unordered Map
- Arrays
- Pointers
- Integer Division
- Tree
- Arithmetic
- Vector
- Graphs
- Higher Order Function
- Interfaces
- OOP
- Exceptions
- Inheritance
- Method Overriding
- Hash and Equals
- Queue
- Iteration
- Map
- Stream
- Strings
- Memory Management
- Dynamic Programming
- Regex
- Linked List
- Conditions
- Sorting
- Complexity
- Stack
- Pass by Reference
- Destructors
- Random
- Recursion
- Data Structures
- Video
- AI Code Review
- Conditional Statements
- Loops
- Abstract Class
- Unordered Set
- Classes
For job roles
- Back-End Developer
- C++ Developer
Sample candidate report
Need it fast? AI-crafted tests for your job role
TestDome generates custom tests tailored to the specific skills you need for your job role.
Sign up now to try it out and see how AI can streamline your hiring process!
What others say
Simple, straight-forward technical testing
TestDome is simple, provides a reasonable (though not extensive) battery of tests to choose from, and doesn't take the candidate an inordinate amount of time. It also simulates working pressure with the time limits.
Jan Opperman, Grindrod Bank
Product reviews
Used by
Solve all your skill testing needs
150+ Pre-made tests
130+ skills
AI-ready assessments
How TestDome works
Choose a pre-made test
or create a custom test
Invite candidates via
email, URL, or your ATS
Candidates take
a test remotely
Sort candidates and
get individual reports

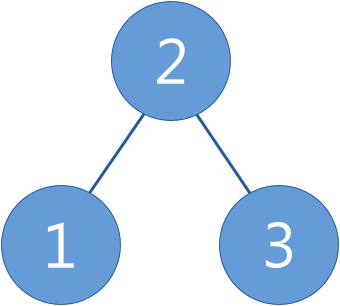 Binary search tree (BST) is a binary tree where the value of each node is larger or equal to the values in all the nodes in that node's left subtree and is smaller than the values in all the nodes in that node's right subtree.
Binary search tree (BST) is a binary tree where the value of each node is larger or equal to the values in all the nodes in that node's left subtree and is smaller than the values in all the nodes in that node's right subtree.